hypermobility in babies ankles
A short video clip from Podiatrist Andrew Bull a member of our health professional network on foot ankle pronation and hypermobility. Frequent joint dislocations and subluxations partial dislocation often affecting the shoulder kneecap andor temporomandibular joint joint that connects the lower jaw to the skull.

When To Brace Kids With Low Muscle Tone And Pronation Surestep
The term generalised joint hypermobility GJH is used when a child has several joints that are more flexible than usual.

. Baseline data included Beighton score BMI for age Star Excursion Balance Test SEBT Foot Posture Index FPI anterior drawer subtalar. Hypermobility can be associated with recurrent pains at the end of the day or at night in the knees feet andor ankles. In adolescent girls there is a peak at the age of fifteen years after this age the joint mobility decreases as well in boys as in girls.
Mechanical causes are frequently identified and hypermobility or ligamentous laxity of joints is increasingly recognized as an aetiological factor in the. It might affect the fingers and hands. For most children hypermobility affects just the joints.
It is not unusual to have a few hypermobile joints. The late Dr Barbara Ansell frequently stated that hypermobility is tricky in children. The ability of a joint to move beyond its normal range of motion is joint hypermobility.
Rarely mild joint swelling may come and go but does not tend to persist. When we are babies we are very flexiblewhich is perfectly normaland this flexibility usually reduces as we age. Some children as are also.
Infants with joint hypermobility have joints that are able to bend further than usual and a trunk and limbs that appear to be floppy and weak. In infants with joint hypermobility the connective tissue that holds the muscles together and connects the muscles to the bones via the tendons is very pliable. 4 points hypermobility likely.
The knee ankle and shoulder are the most commonly affected joints in children. Sensible footwear choices are extremely important and simple changes here can make a significant difference to many people with hypermobility. Braces for the older child involved in sport soft braces to protect knees or ankles are sometimes recommended.
Generalised joint hypermobility is quite a common occurrence - in fact it is just a normal. However in some people hypermobile joints can cause joint pain and result in higher rates of. In most people this causes no problems and does not require treatment.
The pain is more common in the legs such as the calf or thigh muscles. Joint hypermobility in babies and children is even more common and usually causes no problems. 4 points and pain in 4 or more joints for at least 3 months joint hypermobility syndrome likely.
HSDs are the diagnosis where the main or only symptoms are exercise-related pain together with joint hypermobility. Bend a little finger back more than 90 degrees. The increased range of movement at the joints sometimes called joint laxity or being double jointed is due to differences in the connective tissue that forms the joint capsule and ligaments.
Foot Ankle Pronation in Hypermobility. This happens when the connective tissue which makes up the joint structures capsule and. Joint hypermobility and musculoskeletal injury.
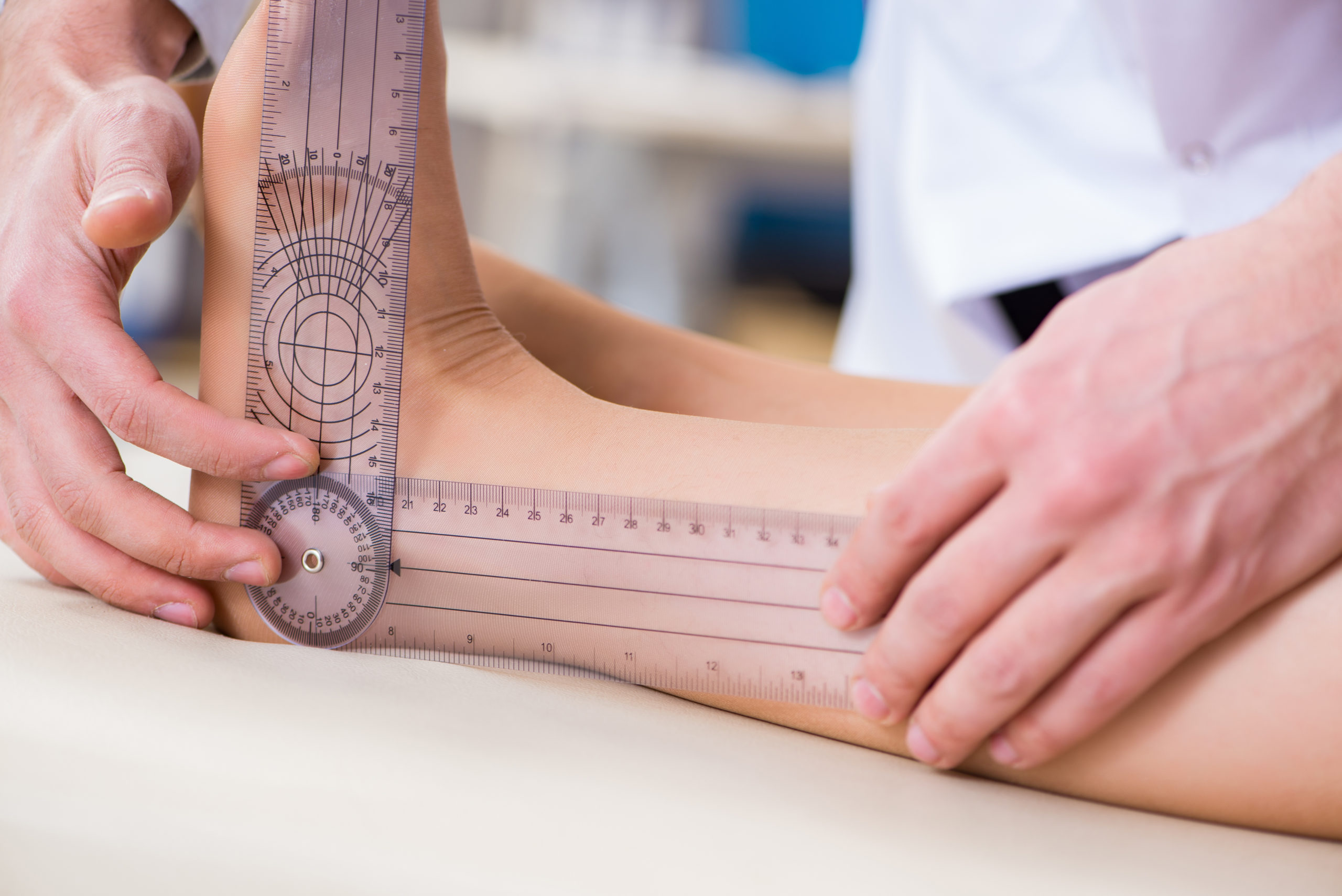
You will see in the video 2 black lines on the patients ankles. Benign hypermobility describes a child that has several joints that are more flexible than usual. If the sensitivity to stretch is very low the muscles are slow to respond and they appear to be weak and floppy.
In infants with joint hypermobility the connective tissue that holds the muscles together and connects the muscles to the bones via the tendons is very pliable. Joint hypermobility without pain occurs when children have stretchy or flexible joints but without exercise-related pain. Bend a thumb backwards to touch your forearm.
Joint hypermobility happens most often in children and reduces with age. Joint instability and injury is more common in people with joint hypermobility. This affects the sensitivity of the stretch receptors and the muscles readiness for action.
This is an advantage to some children and tends to be associated with being good at sport. Joint hypermobility affecting both large elbows knees and small fingers toes joints. Of these 100 children 94 met the Brighton criteria for Joint Hypermobility Syndrome and 90 met the Villefranche criteria for Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome-Hypermobility Type Of the entire cohort 50.
It is sometimes referred to as being double jointed and is quite common about 1 in 10 people are hypermobile. As children with hypermobile joints require added support around the heel and ankle the shoes should have a closed solid and ideally high heel cap. 62 rows The signs and symptoms of hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome vary but may include.
Joint mobility is highest at birth there is a decrease in children around nine to twelve years old. While standing put hands flat on floor while knees stay straight. That joint hypermobility should more frequently occur in children than in adults is undoubted.
It is well recognized that many if not most children and adolescents attending paediatric rheumatology clinics will have a non-inflammatory origin for their complaints or disorder. However some children have a condition called Joint Hypermobility Syndrome or JHS. But when hypermobility causes pain it could point towards joint hypermobility syndrome which needs to be treated.
Children or young adults with hypermobility have joint pain. Most people with hypermobility will not find a genetic cause but early identification means that steps can be taken to minimise injury. In addition to hypermobile joints a child with JHS may also have.
Unstable ankles and overly flexible feet can benefit from greater control provided by the shoe and the impact of overloaded joints and soft tissues can be offset to a significant degree through the judicious use of shock-absorbing. This is normally attributed to the stabilization of joint collagen that occurs as a result of increased cross-linking between adjacent molecules as disulphide bridges form with ageing. This happens when the connective tissue which makes up the joint structures capsule and ligaments is more compliant more easily stretched than usual.
One way to check if the heel cap is solid is by pressing your thumb against the back. If you watch these closely when the patient steps off the orthotics you can see that the angle. Children with hypermobility Beighton score 49 were recruited for a longitudinal study from The Childrens Hospital at Westmead in Sydney Australia.
As she got older she would sit in the w position and sleep with her legs in the same position shes now 7 and has problems running her feet ankles and hips are turning and we only got a dx of hypermobility a month ago as the GP would not listen to me shes now waiting for physio and insoles for her shoes shes also having OT weekly. The term benign hypermobility joint syndrome BHJS is a common source of joint or muscle complaints that often cause concern for parents children and school personnel. It most often involves large joints such as the knees or elbows.
Joint hypermobility can differ between individuals depending on their genes age and race. Foot and ankle complaints are common in people with hypermobility. Being extremely flexible and having pain associated with this flexibility could indicate that your child is hypermobile.
This can be very common in children 10-15 and usually decreases with age.
Living With A Hypermobile Toddler
Joint Hypermobility Kids Adults My Footdr

Flat Feet Not Just A Foot Problem Skills For Action
Living With A Hypermobile Toddler

Leg Braces For Kids How They Can Help Your Child Thrive Surestep

How Hypermobility And Low Muscle Tone Affect Your Baby S Development Skills For Action

Hypermobility Syndrome Therapies For Kids

My Child Is Very Flexible Is This Normal Sole Motion Podiatry
Living With A Hypermobile Toddler
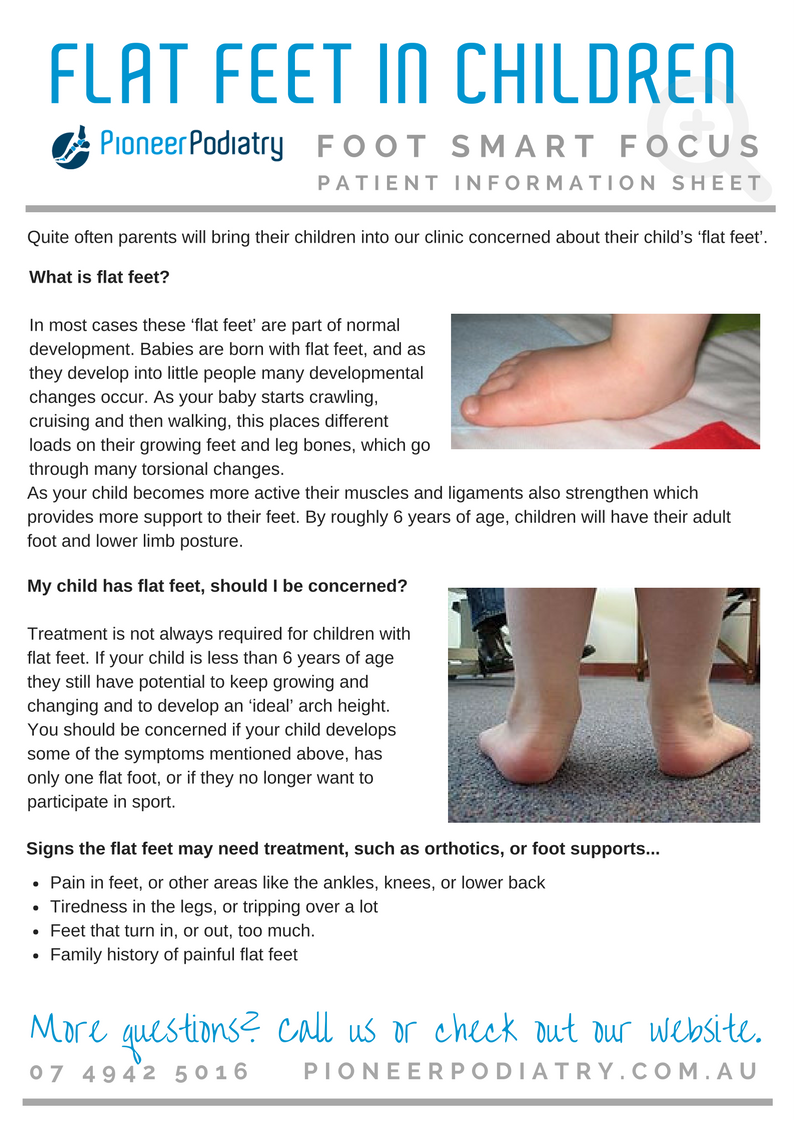
Pioneer Podiatry Portal Flat Feet In Kids

What Is Hypermobility In Babies Children Young Adults Therapy Stars

How To Recognise Joint Hypermobility In Your Child My Strong Little Body

The Best Shoes For Kids With Hypermobility Extra Arch And Ankle Support Fitting Children S Shoes

If Your Child Has Flat Feet Then There Main Be Chances Of Foot Pronation Distortion Syndrome Read This Blog Pronation Muscle Imbalance Syndrome

Kids Flat Feet Point Cook Should My Kids Feet Be So Flat Sole Motion Podiatry

What Is Hypermobility In Babies Children Young Adults Therapy Stars

Treatment For Flat Feet Therapies For Kids
Joint Hypermobility Kids Adults My Footdr

How Hypermobility And Low Muscle Tone Affect Your Infant S Development Low Muscle Tone Pediatric Physical Therapy Baby Development